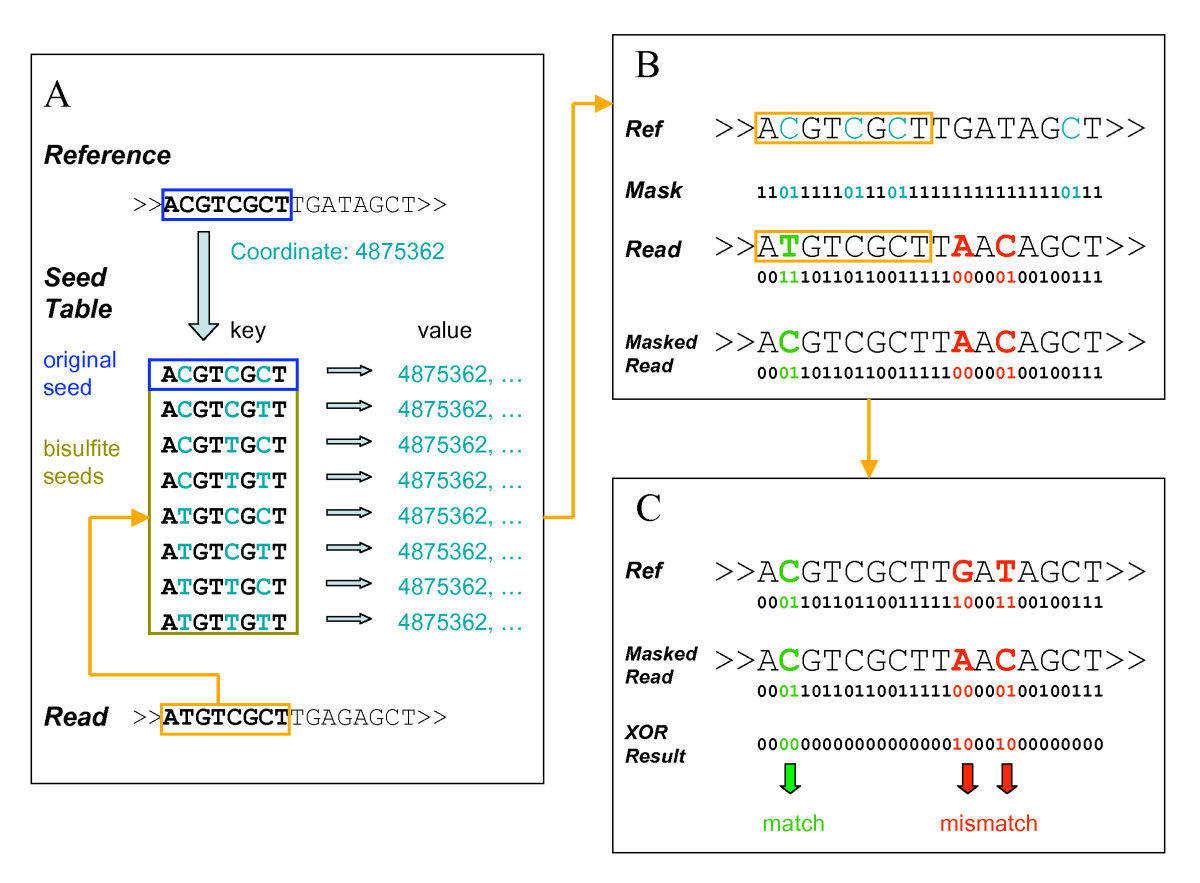
基因印迹 Interaction between DNA methylation, histone modifications, and other players such as non-coding RNAs Cell and tissue type specificity Gene-environment interaction, disease susceptibility 基本原理 比对的过程需要进行转换 常用 mapping 软件算法 Bisulfite seed table, using the original seed and bisulfite variants as keys and corresponding coordinates in the reference genome as values. Each read was looked up in the seed table for potential mapping positions. A positional specific mask of the corresponding reference sequence was generated by setting 01 to C(light blue) and 11 to A, G, T(black). The original read was masked by a bitwise AND operation with the positional specific mask. The reference sequence and the masked read were compared with a bitwise XOR operation. Non-zero XOR results were counted as mismatches (red). Bisulfite alignment is marked in green. Unmethylated CpGs are identified by sequencing size selected fragments from parallel DNA digestions with the methyl-sensitive restriction enzymes (MREs) 没有甲基化的地方会有 peak 甲基化敏感性限制酶测序 (MRE-seq) 技术主要利用甲基化敏感性限制性酶 (methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme, MRE) 对基因组 DNA 进行切割,未甲基化位点可以被酶切而产生不同长度的片段,然后,结合高通量测序技术获得序列的甲基化信息 和 MeDIP 结合使用 plant DOI:10.1146/annurev-arplant-043014-114633 human DOI:10.1038/nature08514 半自动基因注释 两种常用算法 输入参数 算法是 HMM,具体隐马尔可夫模型参考另一篇笔记 属于 HMM 中的 learning 类问题 使用迭代方法是 EM 200 bp resolution Bernoulli to model emission Posterior decoding Single model for all cell types 具体学习地址 本文作者:思考问题的熊 版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议 (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) 进行许可。 如果你对这篇文章感兴趣,欢迎通过邮箱订阅我的 「熊言熊语」会员通讯,我将第一时间与你分享肿瘤生物医药领域最新行业研究进展和我的所思所学所想,点此链接即可进行免费订阅。不同层次的表观
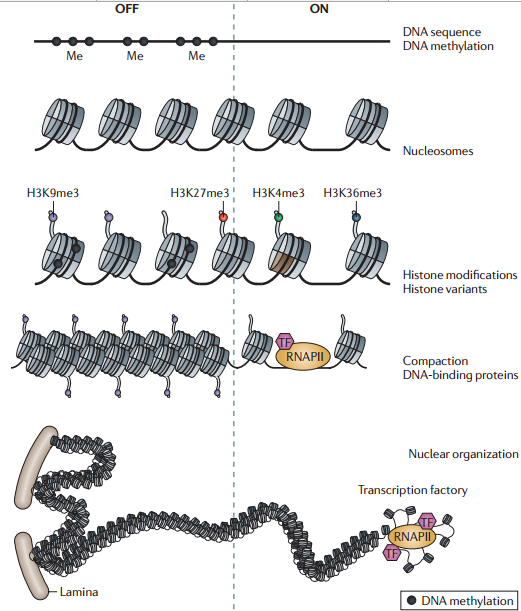
表观实例
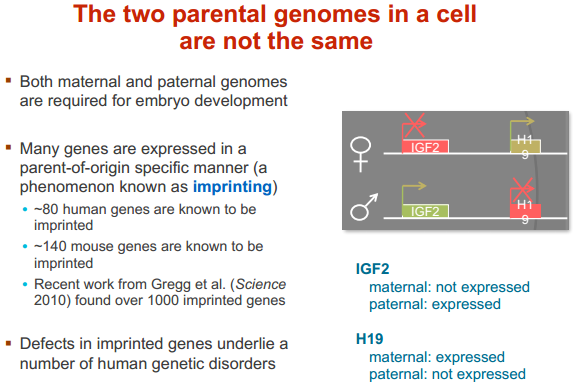
表观遗传定义
表观基因组 epigenome
Epigenetic mechanisms
DNA methylation
Histone modification
DNA methylation
human 特征
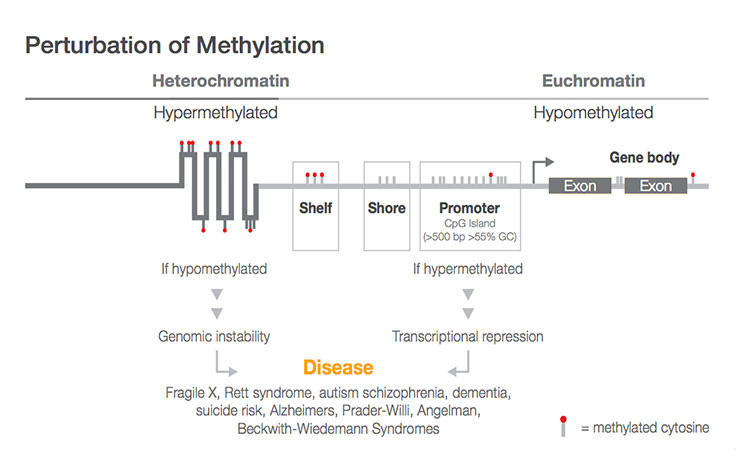
植物中有特殊的 RdDM
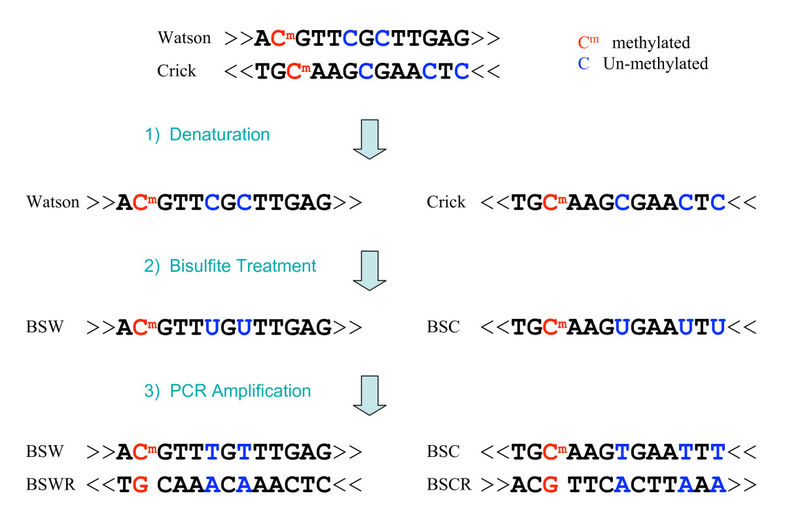
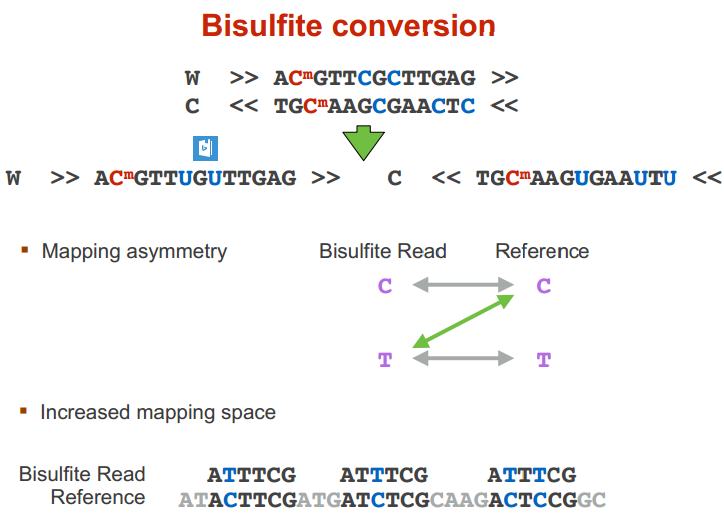
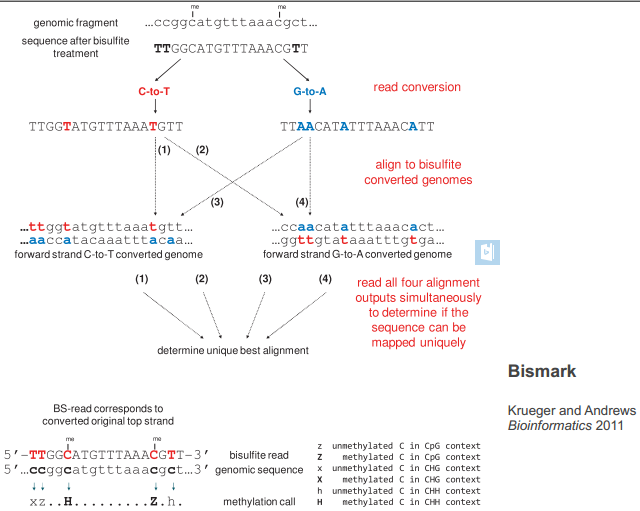
bisulfite sequencing
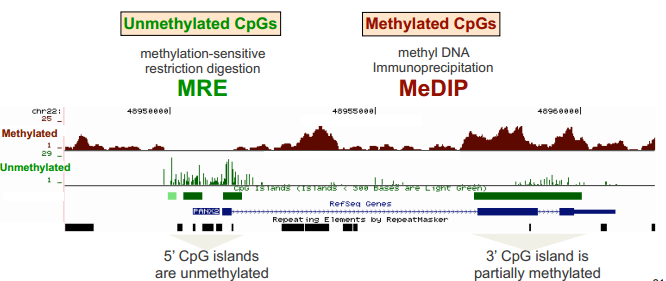
Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP)
Methyl-sensitive restriction enzymes (MREs)
组蛋白修饰
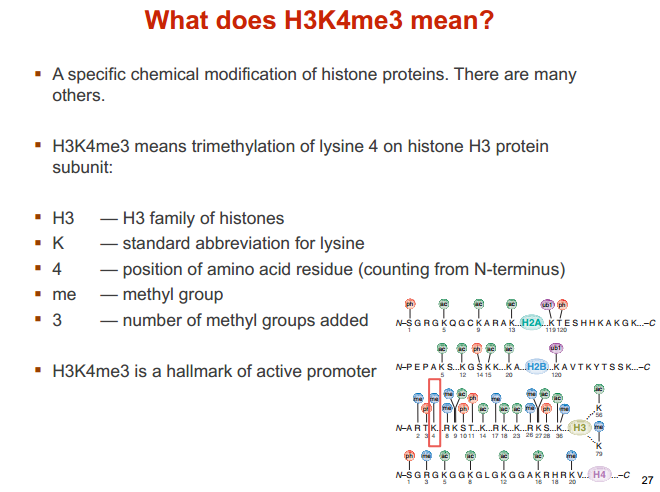
H3K4me3 含义
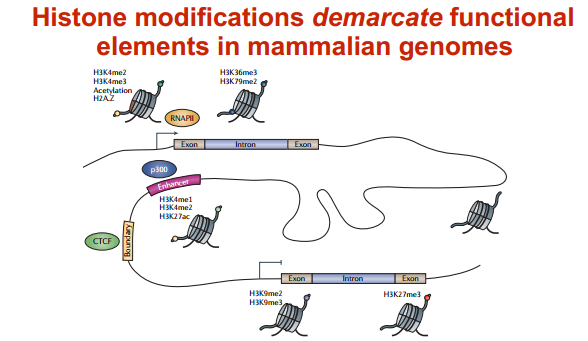
组蛋白修饰功能
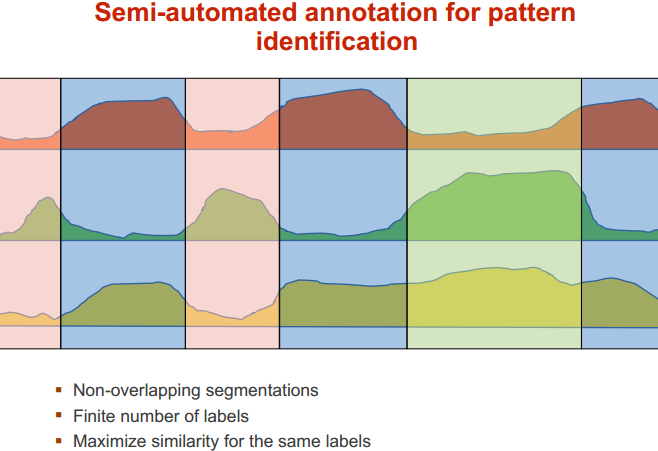
如何整合众多的 ChIP-seq 数据
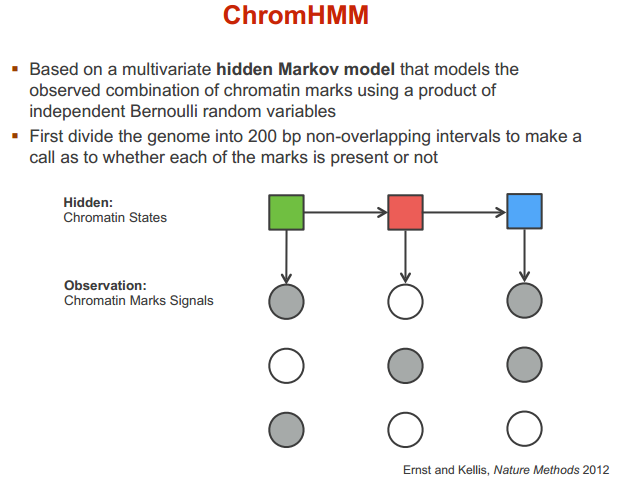
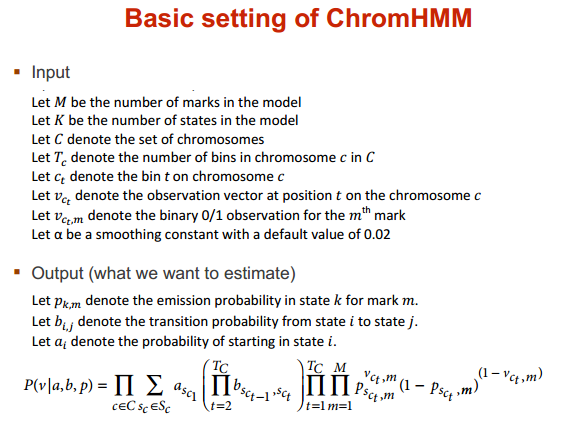
ChromHMM
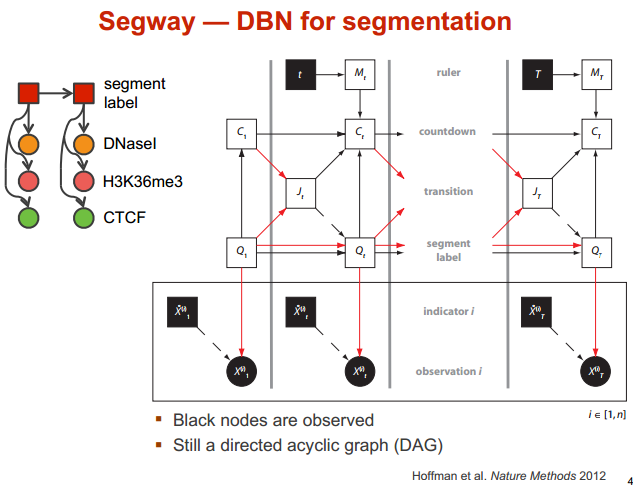
Segway
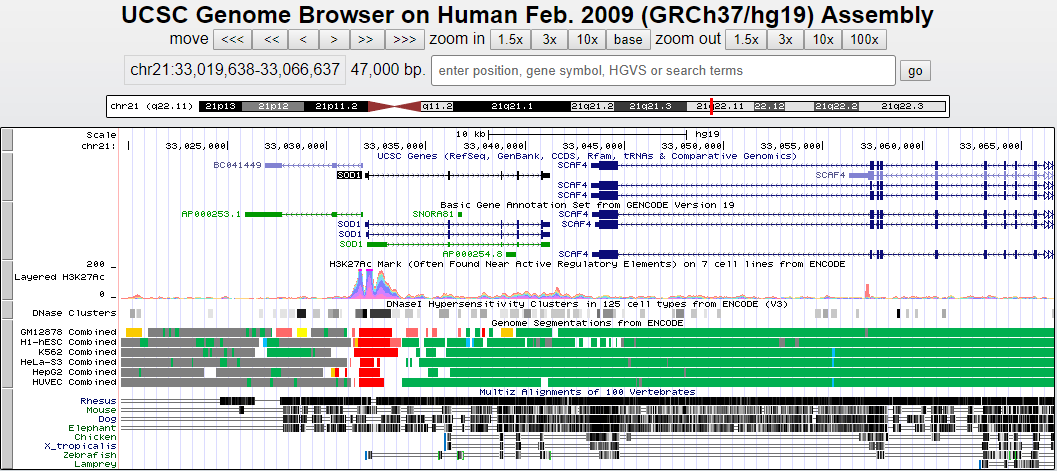
基因浏览器展示
human 表观数据库
encode
roadmap
· 分享链接 https://kaopubear.top/blog/2017-08-17-longxing-bioinfo-epigenetic/